ISDN is a telephone system network. the phone system was viewed as a way to transport voice, with some special services available for data. The key feature of the ISDN is that it integrates speech and data on the same lines, adding features that were not available in the classic telephone system.ISDN allows multiplexing of devices over single ISDN line
ISDN is a circuit-switched telephone network system, that also provides access to packet switched networks, designed to allow digital transmission of voice and data over ordinary telephone copper wires, resulting in better voice quality than an analog phone. It offers circuit-switched connections (for either voice or data), and packet-switched connections (for data), in increments of 64 kbit/s. Another major use case is Internet access, where ISDN typically provides a maximum of 128 kbit/s in both upstream and downstream directions (which can be considered to be broadband speed, since it exceeds the narrowband speeds of standard analog 56k telephone lines). ISDN channels may use bonding to achieve a greater data rate, typically 3 or 4 BRIs (6 to 8 64 kbit/s channels) are bonded.
In a broad sense ISDN can be considered a digital communications medium existing on layers 1, 2, and 3 of the OSI model. ISDN is designed to provide access to voice and data services simultaneously.
(a)Types of channels:
1. Bearer channel (B-channel=64 kb/s) clear pipe for data
2. Delta channel (D-channel, 16 kb/s or 64 kb/s) call signaling information:
o who is calling
o type of call
o calling what number
(b) Service types:
1. Basic Rate Interface (2 B channels + 1 D channel (16 kb/s))
2. Primary Rate Interface (30 B channels + 1 D channel (64 kb/s))
1. Basic Rate Interface:
o Digital data exchanged between subscriber and NTE - Full Duplex
o Separate physical line for each direction
o Pseudoternary coding scheme
o 1=no voltage, 0=positive or negative 750mV +/-10%
o Data rate 192kbps
o Basic access is two 64kbps B channels and one 16kbps D channel
o This gives 144kbps multiplexed over 192kbps
o Remaining capacity used for framing and sync
2. Primary Rate Interface:
o B channel is basic user channel
o Data
o PCM voice
o Separate logical 64kbps connections for different destinations
o D channel used for control or data LAPD frames
o Each frame 48 bits long
o One frame every 250ms 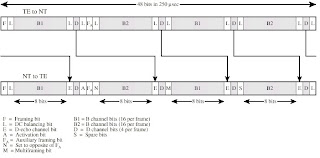
Applications:
Typically supporting PBX
[1] 1.544Mbps
o Based on US DS-1
o Used on T1 services
o 23 B channels plus one D channel
o Line coding is AMI using B8ZS
[2] 2.048Mbps
o Based on European standards
o 30 B channels plus one D channel
o Line coding is AMI using HDB3 
(d)Characteristics:
o Speed(160 kb/s for BRI & 2048 kb/s for PRI)
o Fast call setup(2 Seconds)
o Bandwidth on Demand
o Bandwidth on Demand(adding new channels to the bundle of channels)
o Multiple devices phone(fax, PC, videoconferencing system, router, terminal adapter,.. each with its own sub-address)
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network)
Posted by Creativity by Shakhawat
Labels:
1.544Mbps,
2.048Mbps,
B-Channels,
D-Channels,
ISDN
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


0 comments:
Post a Comment